- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Why Titanium ASTM B265 Gr2 Plates Are Used in Chemical Equipment
Due to their superior mechanical qualities and excellent corrosion protection, Titanium ASTM B265 Gr2 Plates are the foundation of modern chemical equipment. These commercially pure titanium plates are the most durable you can find in harsh chemical settings. This makes them essential for reactor tanks, heat exchangers, and pipe systems. There is no better material for challenging industry uses in the aircraft, petrochemical, and pharmaceutical sectors than these because they are biocompatible, lightweight, and resistant to harsh chemicals.
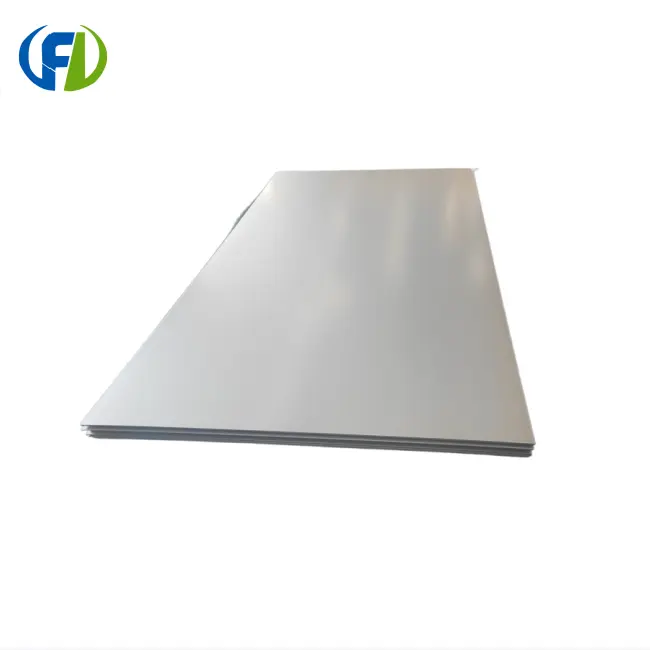
Understanding Titanium ASTM B265 Gr2 Plates in Chemical Equipment
Material Composition and Standards Compliance
As of now, ASTM B265 Grade 2 is the most common standard for commercially pure titanium used in business. Based on what the American Society for Testing and Materials says, this material has a minimum of 99% titanium and limited amounts of iron, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. The basic make-up has an iron content of no more than 0.30%, a carbon content of no more than 0.08%, a nitrogen content of no more than 0.03%, and an oxygen content of no more than 0.25%. These exact compositional standards make sure that performance factors stay the same from one batch of manufacturing to the next.
The standard includes both ASTM B265 and ASME SB265 requirements, so it can be used in both types of pressure vessels. During production, factories must follow strict quality control rules. These rules include heat treatment methods that improve the texture of the material. The titanium plates that were made have a uniform grain structure and known mechanical qualities that are important for chemical processes.
Mechanical Properties and Performance Characteristics
With a minimum yield strength of 275 MPa (40 ksi) and a maximum tensile strength of 345 MPa (50 ksi), Grade 2 titanium plates are very strong. These qualities are better than those of many common materials, and they still allow for great ductility and 20% elongation. The material's mass of 4.5 g/cm³ makes it much lighter than stainless steel options, which lowers the loads on equipment that supports the structure.
Temperature performance stays the same over a wide range of applications. For example, Grade 2 titanium keeps its shape at high temperatures that are common in chemical processes. The material is very good at resisting stress when loaded and unloaded many times. This means it can be used in equipment that is heated or cooled many times. These technical features work together to provide dependable long-term performance in tough industrial settings.
Quality Assurance and Testing Protocols
During the whole process of making ASTM B265 Gr2 titanium plates, strict testing methods make sure that their quality and stability are maintained. Chemical research confirms that the elements are within certain limits, and mechanical testing shows that the required strength and ductility have been met. Some types of nondestructive testing, like laser screening and surface examination, can find flaws that might affect performance.
Each package comes with certification paperwork that lets you track it all the way from where the raw materials came from to how they were finished. For quality assurance, mill test papers for the Titanium ASTM B265 Gr2 Plates list the chemical make-up, mechanical features, and size requirements. These thorough quality control steps make sure that the products that buying teams get meet all the requirements of the project and the standards of the industry.
Applications and Benefits of ASTM B265 Gr2 Titanium Plates in Chemical Equipment
Primary Industrial Applications
Chemical processing plants use Grade 2 titanium plates a lot in the building of reactors because they work better in settings that are corrosive. These plates are used as electrolytic cell parts in chlor-alkali plants because titanium doesn't rust when exposed to chlorine. Titanium plates are used in clean processing tanks on pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment to keep them from getting contaminated.
When used in heat exchangers, titanium is useful because it is a good thermal conductor and doesn't rust. These features are used by seawater cooling systems, especially in offshore petrochemical sites, to keep operations running smoothly and reduce the amount of upkeep that needs to be done. Because the material doesn't react badly with harsh chemicals, it makes tools last a lot longer than with standard materials.
Corrosion Resistance Advantages
Grade 2 titanium is very resistant to corrosion because it can make a protective oxide layer when it comes in contact with air. Most acids, such as hydrochloric, sulfuric, and nitric acids at different temperatures and amounts, can't damage this passive film. While chloride settings can cause pitting and crevice rust in stainless steel, these conditions don't affect the surface structure of titanium.
Chemical compatibility includes organic solvents, oxidizing agents, and alkaline solutions that are used in many industrial processes. The substance doesn't crack under stress, which is a way that many other materials fail in high-stress chemical settings. This all-around resistance to corrosion means lower upkeep costs, longer machine life, and more reliable processes.
Economic and Performance Benefits
The starting cost of materials for titanium plates is higher than for other materials, but titanium has a lower total cost of ownership in demanding uses. Longer service lives mean that parts don't have to be replaced as often, which cuts down on the time that is lost for upkeep. Because titanium is so light, it doesn't need as much support, which could lower the total cost of building.
Titanium's smooth surface finish, as seen in Titanium ASTM B265 Gr2 Plates, makes processes more efficient because it keeps heat transfer working well over time and doesn't get clogged up. Because it is easier to clean and doesn't react with chemicals, there is no need for expensive coats or rust inhibitors. These practical benefits add up to big savings over the life of the tools, which makes the higher material investment worthwhile.
Selecting and Procuring ASTM B265 Gr2 Titanium Plates for Chemical Equipment
Technical Selection Criteria
In order to choose the right material, you need to carefully consider the working conditions, such as the temperature ranges, chemical exposure, and mechanical loading needs. Process engineers need to think about the corrosive climate because some harsh media may need higher grades of titanium or special metals. Dimensional standards, such as tolerances for width and surface finish, affect both function and the ability to make the product.
Weldability standards are part of the design process, and Grade 2 titanium has great welding properties when used correctly. Lead times and prices are affected by how complicated the fabrication is, so it's best to involve suppliers early on for complex shapes. Certifications for materials must match the relevant rules and codes, especially for uses with pressure vessels that need to meet ASME standards.
Supplier Evaluation and Quality Verification
To find good titanium plate suppliers, you need to carefully look at their manufacturing skills, quality control methods, and knowledge in the field. Established suppliers have full quality control systems that are approved to meet international standards like AS9100 and ISO 9001. Advanced melting technologies, such as vacuum arc remelting, should be used in production sites to make sure that materials are pure and consistent.
When evaluating a supplier, customer examples from similar projects should be looked at. This is especially important in chemical processing businesses. Quality documentation tools, such as proof of compliance and material tracking systems, show how knowledgeable and trustworthy a provider you are. Technical support services, like metallurgical advice and application engineering help, make the connection with the provider much more valuable.
Procurement Process and Logistics
Titanium has unique manufacturing needs and longer wait times than other materials, but good purchase planning takes these into account. Order amounts should balance the costs of keeping inventory with the benefits of bulk prices, since titanium production usually requires a minimum order size. When planning deliveries, it's important to take into account production cycles and project deadlines.
When you source from other countries, you need to pay attention to export laws and paperwork needs, especially for defense and aircraft uses, such as with Titanium ASTM B265 Gr2 Plates. The rules for packaging should protect the surfaces of the materials during shipping and make it easier to check the quality when they arrive. Total buying costs are affected by payment terms and currencies, especially when large amounts are bought or long-term supply deals are made.
Conclusion
Titanium ASTM B265 Gr2 plates are widely used in chemical equipment because they are the most corrosion-resistant, reliable, and cost-effective materials available. Innovative chemical processing solutions are still possible with these materials, and they also have long-term operating benefits like lower upkeep needs and longer service lives. To make execution work, you need to pay close attention to the criteria for choosing materials, the steps for qualifying suppliers, and the steps for checking the quality. Investing in high-quality titanium materials pays off by making the process more reliable, cutting down on downtime, and improving safety in a wide range of chemical handling situations.
FAQ
1. What distinguishes Grade 2 from other titanium grades in chemical applications?
The best mix of corrosion protection, mechanical strength, and cost-effectiveness for most chemical handling tasks can be found in grade 2 titanium. Although Grade 1 is a little easier to shape, Grade 2 is much stronger, which is important for building uses. Compared to Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V), Grade 2 is better at resisting rust in a wide range of chemical conditions while still being easy to weld.
2. How do differences in size affect how well chemical equipment performs?
Dimensional accuracy has a direct effect on how well equipment is put together, how well it seals, and how reliable it is in use. Standard ASTM B265 tolerances are good for most uses, but for important closing areas, tighter specs may be needed. Precision rolling and cutting are two of the things we can do to meet your exact size needs while keeping the material's features the same across the thickness.
3. What certification documentation accompanies titanium plate shipments?
Mill test certificates that list the chemical make-up, mechanical qualities, and size data are part of full certification packages. Documentation for quality assurance includes records of heat treatment, reports of nondestructive testing, and checks of the surface state. If asked during the buying process, extra certifications like NACE compliance or customer-specific standards can be given.
Partner with Freelong for Premium Titanium Solutions
Baoji Freelong New Material Technology Development Co., Ltd. can help you with your chemical equipment projects by making high-quality ASTM B265 Gr2 titanium plates that are exactly what you need. Our technical know-how, thorough quality control, and ability to handle operations around the world make sure that you can always get the materials you need for even the most difficult projects. Email our engineering team at jenny@bjfreelong.com to talk about your unique needs and get prices that are made to fit your project. As a reputable company that makes titanium ASTM B265 Gr2 plates, we offer reasonable pricing, expert support, and sample shipping to show that we are dedicated to providing high-quality materials and excellent customer service.
References
1. Boyer, R. R. "An Overview on the Use of Titanium in the Aerospace Industry." Materials Science and Engineering: A, Vol. 213, 1996, pp. 103-114.
2. Schutz, R. W. "Corrosion of Titanium and Titanium Alloys in Chemical Process Industries." Industrial Corrosion, Vol. 18, No. 2, 2000, pp. 145-162.
3. American Society for Testing and Materials. "Standard Specification for Titanium and Titanium Alloy Strip, Sheet, and Plate." ASTM B265-20a, West Conshohocken, PA, 2020.
4. Donachie, Matthew J. "Titanium: A Technical Guide." ASM International Materials Park, Ohio, Second Edition, 2000.
5. Cotton, J. D. "Selection and Application of Titanium Alloys for Chemical Process Equipment." Process Safety Progress, Vol. 28, No. 4, 2009, pp. 234-241.
6. Peters, M., Kumpfert, J., Ward, C. H., and Leyens, C. "Titanium Alloys for Aerospace Applications." Advanced Engineering Materials, Vol. 5, No. 6, 2003, pp. 419-427.

Learn about our latest products and discounts through SMS or email
_1745897023856.webp)
_1745573568694.webp)
_1744967365184.webp)
_1745227752700.webp)